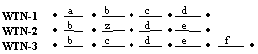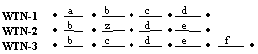rover
WORK IN PROGRESS
rover - Recognition Output Voting Error Reduction
rover [ -sT -a alpha -c Nconf -f level -l width ] ( -h hypfile ctm )+ -o outfile -m meth
Input Options
-h hypfile ctm
Define the hypothesis file and it's format. This option
must be used more than once. Currently, only the ctm format
is recgnized.
Output Options
-o outfile
Define the output file. (Will be same format as hyps)
-f level
Defines feedback mode, default is 1
-l width
Voting Options
-m meth
Set the voting method 'meth' to one of the following:
oracle -> output the fully alternated transcript
meth1 -> alpha = -a , conf = -c, choose highest avg
maxconf -> Voting by Using Maximum Confidence Score
avgconf -> Voting by Average Conf. Score
maxconfa ->
Same as maxconf, but set the confidence score for
the NULL transition arcs to be the number of NULL transition
arcs in the correspondence set divided by the number of input
systems.
putat -> Output the putative hit format
-a alpha Set Alpha to 'alpha'. Alpha is the tradeoff between
using word occurrence counts and confidence scores.
By default alpha is 1.0
-c Nconf
Set confidence score associated with NULL transition
arcs to 'Nconf'. Default: 0.0
Alignment Options
-s
Do Case-sensitive alignments.
-T Use time information, (if available), to calculated word-to-
word distances.
Rover is a tool combine hypothesized word outputs of multiple
recognition systems and select the best scoring word sequence.
Rover is part of the NIST SCTK Scoring Tookit. A
number of different output formats can be generated and different
scoring functions can be specified. A more complete description of
the rover system can be found in the paper
A post-processing system to yield reduced word error rates: Recognizer
Output Voting Error Reduction (ROVER).
The ROVER system is implemented in two modules. First, the system
outputs from two or more ASR systems are combined into a single word
transition network. The network is created using a modification of the
dynamic programming alignment protocol traditionally used by NIST to
evaluate ASR technology. Once the network is generated, the second
module evaluates each branching point using a voting scheme, which
selects the best scoring word (with the highest number of votes) for
the new transcription. The following figure depicts the the overall
system architecture.
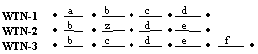
The heart of the Rover program is the ability to combine system
outputs of mulitple recognition systems using an iterative Dynamic
Programming alignment protocol into a single, composite Word
Transition Network (WTN). The protocol is fully described in the
Section 2.1. RECOGNITION OUTPUT ALIGNMENT MODULE of the paper.
Once the composite WTN is produced, each correspondence set (CS) is
evaluated using the selected scoring function. Section 2.2. WTN VOTING SEARCH
MODULE: describes the voting process in detail.
There are three voting schemes described in the paper:
By Word Frequency
To use word frequency as the scoring function, use the options
'-m avgconf -a 1.0 -c 0.0'. By setting -a to 1.0, the tradeoff
between word occurrences and confidence scores, only the
word occurrences are used.
REVISION HISTORY
This is the initial release.
BUGS/COMMENTS
Please contact Jon Fiscus at NIST with any bug reports or comments at
the email address
jonathan.fiscus@nist.gov or
by phone, (301)-975-3182. Please include the version number of rover,
and any other relevant information such as OS, compiler, etc.